The grading and evaluation of diamonds for use as gemstones in jewelry falls under a branch of science called Gemology. The first attempts at a rigorous, systematic grading standard for diamonds were made in the late 19th and early 20thcentury in response to a rapidly growing market for diamonds and subsequent consumer concerns. Robert Shipley, who founded the Gemological Institute of America in 1931, created the standard model and language by which diamonds are assessed to this day. Known as the “the four C’s,” this grading system evaluates diamond gemstones according their four most essential qualities; Color, Cut, Clarity, and Carat Weight.

-Color – The Color grading scale actually measures the lack of color in diamonds, as colorless stones are more valuable. The scale ranges from completely colorless (D-F), near colorless (G-J), faint (K-M), very light (N-R), and light (S-Z).

-Cut – The Cut Grading scale assesses how the shape of a diamond interacts with light to create desirable optical effects. A successful cut highlights a diamond’s natural ability to reflect light by directing it back towards the viewer, referred to as a diamond’s “brightness”. Other optical qualities include “fire,” the amount of white light a diamond scatters into colored light, and “scintillation,” the distribution of sparkles or points of light throughout a diamond. The combination of these three properties determines the diamond’s cut grade, which ranges from Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair, and Poor.
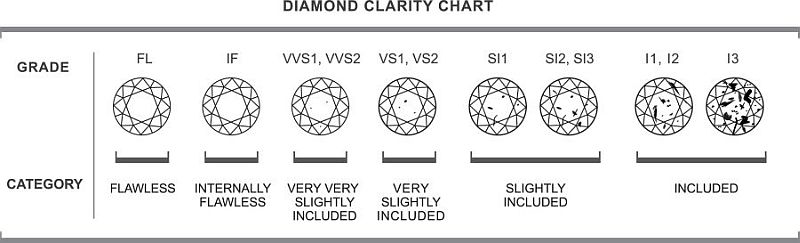
-Clarity- A diamond’s Clarity Grade assesses the presence of imperfections in the diamond, whether they are internal “inclusions,” or external “blemishes”. These can range from crystals or other impurities embedded inside the stone, chips and fractures, pits, laser drill holes, scratching, or polish lines. Often times these imperfections are not noticeable to the naked eye or by one who is not a trained gemologist.
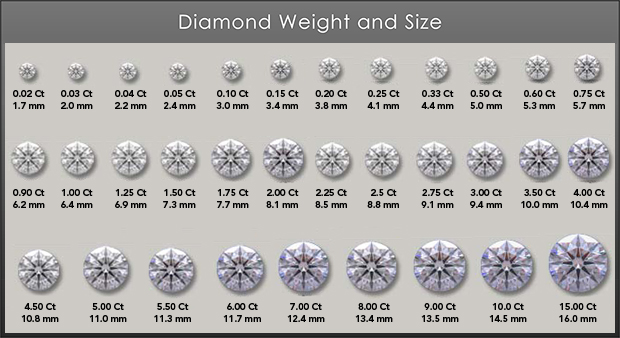
-Carat- The carat grade refers to the overall carat weight of the stone (1 Carat = .2 Grams). While to many folks this comes to mind as the most important determining factor in a diamond’s value, this isn’t always the case. As a general rule, heavier stones are more valuable, but this is in conjunction with all of the other aspects of diamond evaluation. it is possible for two diamonds with equal carat weights to have greatly different values! Sometimes rough diamonds will be cut to emphasize finished weight or size across the top; however this can be to the detriment of the overall appearance and quality of the diamond.
for more info, check out our diamond page!
